The mere mention of body fat conjures images of belly fat, love handles, and extra junk in the trunk. Given that, you will find thousands of articles with exercise tips or diet secrets that promise to lower your body fat percentage and get rid of x amount of body fat in x days.
But what if it is not that simple? What if there is more to body fat than just burning it?
Body fat is something everyone has an opinion on but can be confusing. In fact, some people reason that it is just a natural part of getting older, and if their BMI is in a good range you do not have much to worry about. Specifically, your body does require some body fat to function, but it also requires you to keep your body fat percentage in a certain range for optimal health.
Let us learn what is body fat, how it affects your health, and how you can maintain a healthy body fat percentage.
What is Body Fat?

Body fat is formally known as adipose tissue and consists of smaller components. Of course, to have a better understanding of how to manage your body fat, you first need to know how to talk about it and understand the different types.
The main different types of body fat are as follows:
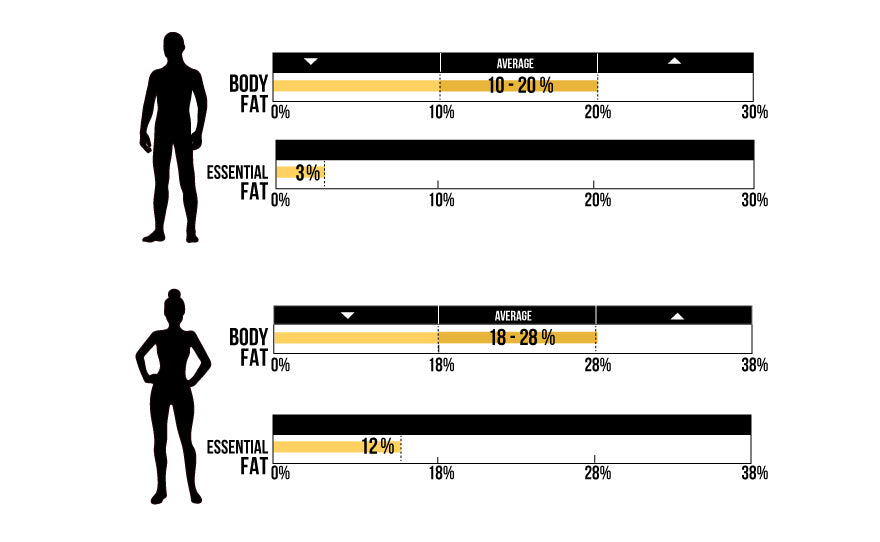
- Essential Fat – found in organs, bone marrow, nerve cells, and the brain and is essential for survival.
- Subcutaneous Fat – located just underneath the skin. It is adipose tissue that you can see, touch, and pinch. Subcutaneous fat is the type of body fat that most people think of when they hear the word “fat” because it is tangible.
- Visceral Fat – the type of body fat that surrounds your organs in your abdominal cavity. BMI measurements often overlook these fat cells in health or body density measurements. However, health professionals recognize visceral fat as a far more dangerous health threat than subcutaneous fat, and it’s considered a strong, independent predictor of all-cause mortality in men and women.
Body Fat Distribution
Many different types of fat make up body fat, each serving different functions. Additionally, body fat distribution differs amongst people and even between men and women. The pattern of fat distribution on a person can indicate a predisposition to certain health conditions.
In general, measuring the waist-to-hip ratio for a person will describe body fat distribution as either:
- Android (apple-shaped) – body fat above the waist
- Gynoid (pear-shaped) – body fat below the waist
Individuals with an upper-body fat pattern, including excess intra-abdominal fat, have significantly increased risk for diabetes, ischemic heart disease, hypertension, and some cancers. As a result, considering your body fat distribution can help you make good decisions about your health and evaluate if you need to make some lifestyle changes to improve your health.
What is Body Fat Percentage?
Body fat percentage is a measure of the total mass of fat divided by the total mass of the body. The human body is composed of many different types of tissues, for example, fat, bone, and different types of muscle. At the same time, much focus exists on how much of the body consists of fat because it greatly impacts the look and functioning of the body.
Why it’s important to know your body fat percentage.
Knowing your body fat percentage gives you trackable health information. Generally speaking, by calculating your body fat percentage, you can identify health risks and pinpoint areas that you may need to address to ensure optimal health. Additionally, since body fat is measurable, you can note the effectiveness of changes you are making in your lifestyle. As a result, you can see your efforts paying off and that will help build momentum.
If you are unsure how to measure your body fat the good news is that there are many ways. From simple caliper measurements to the more high-tech dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) or bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) multiple methods exist to measure body fat. In effect, different methods offer different reliability, ease, and affordability so it makes sense to research your options.
What is a healthy body fat percentage range?
You are probably wondering what the ideal body fat percentage is for men and women. Indeed there are universal standards for ideal body fat percentage values and a few respected organizations have their own recommended ranges.
Healthy Body Fat Percentage Range for Men
For goal setting, the healthy body fat range for men is between 10-20 percent.
These ranges are slightly less forgiving than those set by the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM)—which acknowledges a range of 10-22 percent for men—because they’re centered around an average body fat percentage of 15 percent.
Furthermore, the American Council on Exercise (ACE) has even more lenient ranges, with an average body fat percentage of 21 percent for men.
Healthy Body Fat Percentage Range for Women
A recommended body fat percentage range for women is between 18-28 percent for goal setting.
Again, The ACSM range is more forgiving, with a recommended body fat percentage of 20-32 percent for women. Also, the ACE range is also more accommodating, with an average body fat percentage of 28 percent for women. If you are figuring out the right body composition goal specific to you, these ranges are excellent starting points.
In any event, now that you have defined the healthy range of body fat, let us talk a bit more on the factors that influence increases and decreases of this measurement. By understanding the science behind the numbers, you can make better decisions for your health.
How Do You Gain Body Fat?

Rising obesity is correlated to an increasingly sedentary lifestyle and ultra-convenience. To emphasize, food delivered right to the door, movies at the push of a button, an entire library of information at our fingertips: the examples are endless. It makes sense to examine your lifestyle and ask yourself some important questions.
Put simply: How hard is it to find high-calorie, rich foods? How much exercise do you need to acquire it? On the other hand, how many of us have chronic stress from the hustle and bustle of daily life? In reality, your response to the convenience as well as the stresses of the modern world has an enormous impact on your risk of gaining excess body fat and obesity. No wonder there are more overweight and obese people than ever before.
Fortunately, you still have some control over how you respond by making choices regarding your diet and lifestyle.
What if you have a “slow” metabolism?
It is a common assumption that overweight individuals supposedly have a “slow” metabolism and increase their body fat percentage quickly. Indeed, while there is indeed a connection between metabolism and body composition, you don’t necessarily carry a higher body fat percentage because you’re a slow burner.
As mentioned earlier, genetic influences may be at play in how your body stores fat, yet it is the caloric imbalance over time that is often responsible for your body weight gain.
Overall, your metabolism does not slow down because you are getting older and have consumed more fatty food in your life. Rather, it is largely due to two things that tend to happen as you age, but not because of it—a loss of muscle mass and a tendency towards a sedentary lifestyle.
This is good news for you if you are overweight, because unlike the aging process—which is irreversible—you do have some control over both your muscle loss and your lifestyle habits.
How to Lower Your Body Fat Percentage?
So how do you battle the extra bulge and lower your body fat percentage? By all means, this is one of those things in life where you are already aware of the (sometimes painful) truth, but your mind still wants to believe in a comforting lie, like blaming your weight gain on a slow metabolism.
Eat less. Move more. Of course, no crazy crash diets, no insane exercises, and no “weird tricks.” In theory, it sounds simple.
But we can all agree that it is not as simple as it sounds. Nevertheless, you must take it one (actionable) step after the other if you want to improve your health and become a better version of yourself.
How can you lose weight or lose fat?
There are many ways to create a plan that will help you lose weight or lose fat. To put it this way, get moving. Here are a few ways.
- Strength training/ Resistance training
Weight training is a key component to healthy fat burn as muscular bodies burn more calories. It is like having a higher-revving engine. To point out, the more lean muscle mass you carry, the more calories you burn even at rest, so adding strength and resistance training to your life makes sense.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
High-intensity interval training is a form of exercise where short periods of intense aerobic exercise coupled with a less intense recovery period and that pattern of intense/recovery repeats throughout the workout. In general, these workouts are typically rigorous and effective at burning high numbers of calories. Also, they typically last under 30 minutes.
Calories Burned Leads to Weight Loss
No matter the type of exercise the golden rule is basically to burn calories to aid weight loss. That is to say, creating a calorie deficit leads to the metabolism of fat and ultimately a lower body fat percentage and improved health.
Fat Loss and Caloric Deficit
While calorie counting may have its own set of controversies aiming for a caloric deficit simply works. In fact, it is the basis of nearly every responsible and effective fat loss diet plan. However, eating less does not mean starving yourself and forgetting about nutrition.
It must be remembered, trendy diets are everywhere: keto, plant-based, paleo, Whole30. The list goes on and on. Basically, whatever nutrient-rich diet you enjoy eating, while keeping in mind your overall calorie in and calorie expenditure, should bring you closer to your health goals over time.
Likewise, mindfulness and attention to what you are and are not eating while ensuring that you are getting adequate nutrition is key to a healthy, balanced, weight loss. Notably, a meta-analysis of diet and training programs for weight loss found that combining diet and physical activity is more effective for weight loss over 12 months than interventions based on diet or physical activity alone.
Much research exists to support the fact that exercise and diet must work together for weight loss and body fat. Generally, not one alone is the answer. While diet appears to be the more weighted (no pun intended) factor, exercise has a host of benefits for your body. Exercise offers benefits that diet alone cannot address. For instance, better sleep, lowering visceral fat, and quicker results are all correlated with a diet and exercise regimen. Check out the science
Tracking Your Progress
How do you know that you are on the right track to lower your body fat percentage? Monitoring the scale? In reality, no.
After all, changes in body weight are not exactly an accurate reflection of your progress. A pound of fat weighs the same as a pound of muscle or water in your body. In fact, there are better ways to track your progress to get real-time feedback as to whether your current program works.
A body composition analysis can compute your lean body mass and fat mass. Ultimately, any system you use should distinguish between visceral fat and subcutaneous fat to give you relevant information. The device may even define your Basal Metabolic Rate, a key number to understanding your metabolism.
By paying attention to body composition rather than other measures, you can assess your progress in any diet or exercise program. In essence, the numbers will reflect body changes not necessarily reflected in the mirror, but important to your health.
The Bottom Line
The interplay between caloric imbalance, nutrition, metabolism, exercise regimens – is enough to make anyone’s head spin. In the meantime, once you factor in the role of genetics and environment on obesity, the task to lose body fat can feel overwhelming.
In fact, most people can lose fat and maintain a healthy body fat percentage. However, it is by no means always easy. Find a diet and exercise regimen that helps you control the levels and fits your current lifestyle. It is important to note that numbers on a scale or surface-level fat you can pinch, only portray part of your overall body composition. Therefore, if you rely on appearances only, you may be missing factors that add to your health risk.
Ultimately, taking a body composition test can accurately measure body fat percentage and visceral fat, and that is a crucial step to good health. Know where you stand, and where you need to go. When equipped with full accurate information on your own body, you can make the best decisions for yourself. In any event, your healthy lifestyle is absolutely within reach.